css学习之display、position、float之间的关系
更新日期:
以前在工作中写css时,经常写到或看到这样的代码
.box{display:block;float:left;position:reliative/absoulte;}
这样写元素会如何表现?自己也不清楚,反正只要是各个浏览器上表现正常,是自己想要的效果,便不再深究了。
这种只以结果为导向的做法,当然是不好的,了解display、position、float之间的关系,有助于我们更好的书写css,及明白为什么css排版会如此表现。那么我们今天就来学习一下吧。
其实在w3c规范中是有具体的规定。
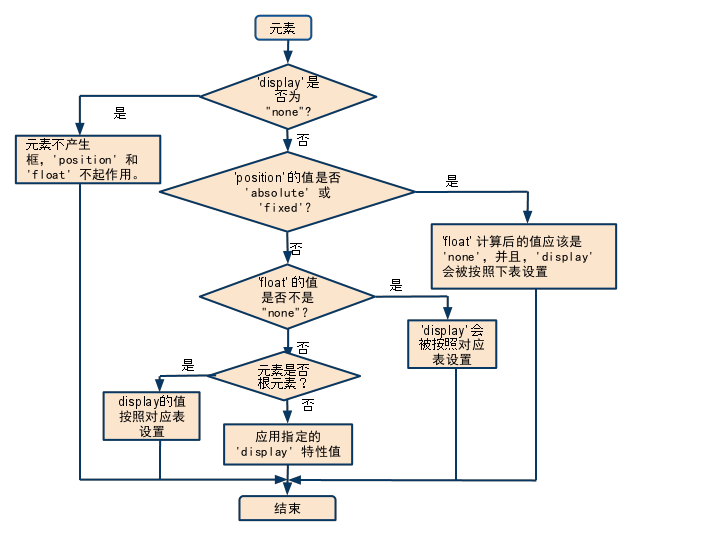
If ‘display’ has the value ‘none’, then ‘position’ and ‘float’ do not apply. In this case, the element generates no box.
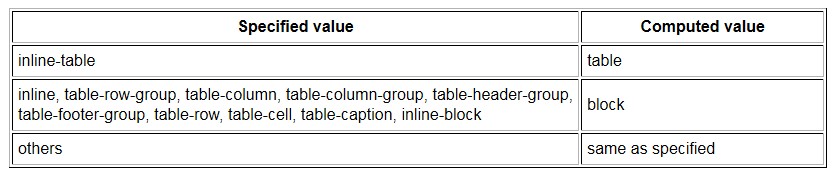
Otherwise, if ‘position’ has the value ‘absolute’ or ‘fixed’, the box is absolutely positioned, the computed value of ‘float’ is ‘none’, and display is set according to the table below. The position of the box will be determined by the ‘top’, ‘right’, ‘bottom’ and ‘left’ properties and the box’s containing block.
Otherwise, if ‘float’ has a value other than ‘none’, the box is floated and ‘display’ is set according to the table below.
Otherwise, if the element is the root element, ‘display’ is set according to the table below, except that it is undefined in CSS 2.1 whether a specified value of ‘list-item’ becomes a computed value of ‘block’ or ‘list-item’.
Otherwise, the remaining ‘display’ property values apply as specified.
1、display:none —> position、float 不起作用。
2、position:absolute/fixed —> float:none, display按下表设置。
3、float:left/right —> display按下表设置
4、float:none —> root元素—> display按下表设置